
Approving Korean nationality acknowledged by the Minister of Justice if not undermining national security, public order, and public welfare. Applicants must have basic knowledge befitting a Korean national such as understanding of the Korean language, customs and culture. Must have the ability to maintain living on his/her own assets or skills or is a dependent member of a family capable of the feat. Must have good conduct defined by the Ministry of Justice decree: compliant with laws and ordinances. Must be legally adult according to Korean Civil Law. Must have a permanent residency (status) in South Korea. Must have had domicile address in R.O.K. Requirements for General Naturalization are as follows (Nationality Act Article 5). Visiting Relatives, Family, Residence, Dependent, and Overseas Koreans. Tourism, Transit, Various Events, and Conferences. Definition and Investigation of Immigration Offender. Refugee Status Application and Determination. Customized Guide for Foreign National Koreans. Scope of Activities for Overseas Koreans. Reporting on Place of Residence: Significance/Procedure. Comprehensive Assessment and Interviews.  Obligation to Choose Nationality/ Procedure to Choose Nationality/ Renunciation Procedure/ Loss of Nationality. Naturalization (General, Simple, Special). Activities not covered by the status of sojourn. Immigration Inspection for Foreign Nationals. Immigration Inspection for Korean Nationals. Confirm e-Application Certificate Issuance. Search Integrated Report of Change in Employment. Registered Agencies for Civil Petitions.
Obligation to Choose Nationality/ Procedure to Choose Nationality/ Renunciation Procedure/ Loss of Nationality. Naturalization (General, Simple, Special). Activities not covered by the status of sojourn. Immigration Inspection for Foreign Nationals. Immigration Inspection for Korean Nationals. Confirm e-Application Certificate Issuance. Search Integrated Report of Change in Employment. Registered Agencies for Civil Petitions.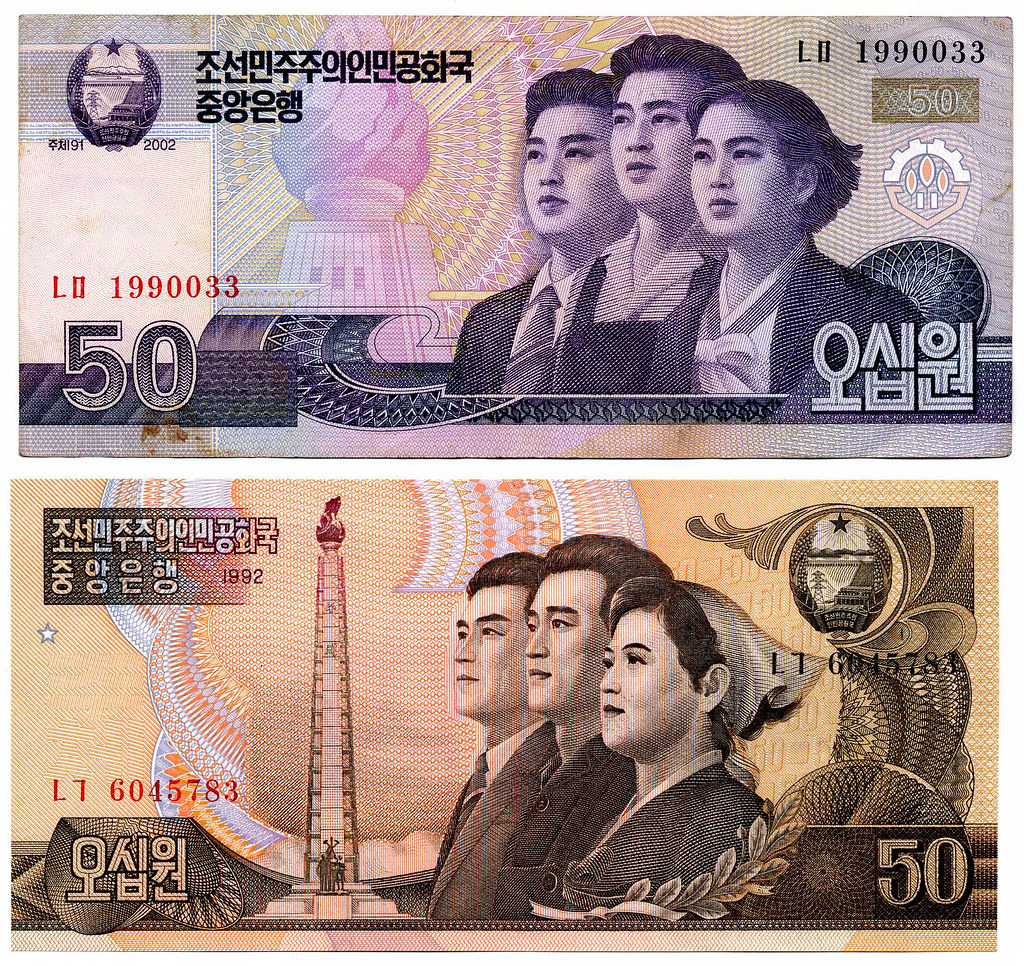  Eligibility check for foreign employment.
Eligibility check for foreign employment. 
Again the Won was fixed to the US Dollar with the peg rate changing multiple times until 1997, when it began to float freely in the market. In 1962, a second Korean Won was established, replacing the Korean Hwan at a rate of 1 KRW to 10 Hwan. In 1953, the Korean Hwan was introduced at a rate of 1 Hwan to 100 Won. Due to the drastic drop in value, the currency was yet again replaced. The Won was originally pegged to the US Dollar at a rate of 15 Won to 1 Dollar, with the peg rate changing multiple times until 1951. Under Japanese rule, Korea was forced to adopt the Korean Yen, replacing the Won at par.įollowing World War II, in 1945, South Korea established the Won as the country’s official currency, replacing the Yen at par. The Bank of Korea was established in 1909, but changed its name to Bank of Joseon when Korea was annexed by Japan one year later. In 1902, the Won was introduced as the official currency of Korea, with an exchange rate of 1 Won to 5 Yang. The Mun was used for over two centuries, until it was replaced in 1892 by the Yang, the first decimalized Korean currency. In 1633, the Korean Mun, made up of copper and bronze coins, was made the principal currency of Korea.







 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
